How hundreds of forgotten klezmer tunes have been rescued from oblivion
Thanks to a mammoth Klezmer Institute digitization project, we can hear Jewish music that hasn’t been played for generations
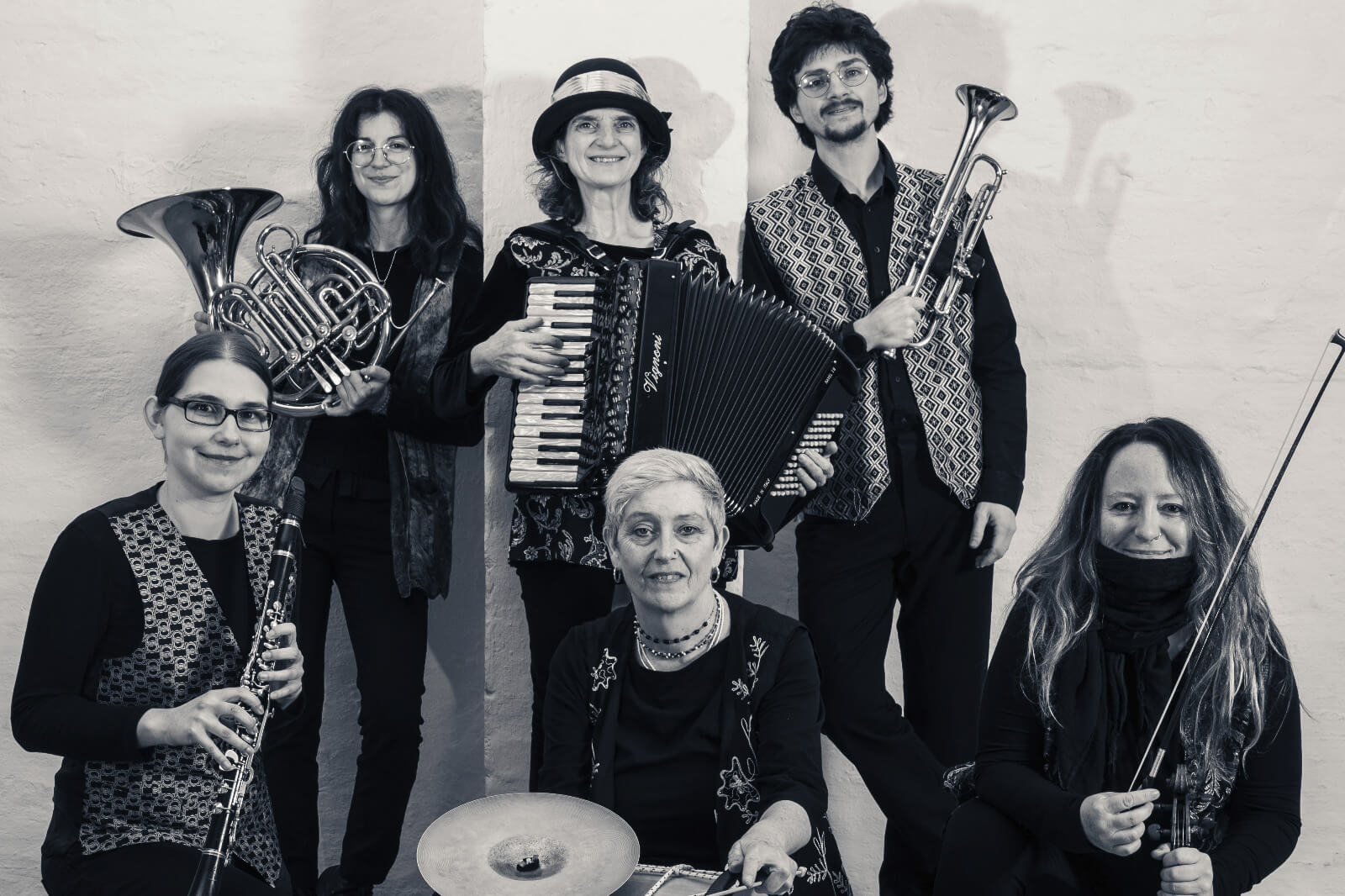

Hop Skotshne is a klezmer ensemble fronted by Hanah Ochner, who has a doctorate in physics. Photo by Agnes Branner
More than one thousand klezmer tunes, some dating back to the late 19th Century, are being performed and recorded after sitting in a library in Kyiv for years, thanks to the nonprofit Klezmer Institute.
“This increases European klezmer music by fourfold over what was accessible before,” Christina Crowder, the New Haven-based accordion player who heads the institute, told me, adding that the collection ranges from virtuosic solo pieces to “workaday, regular old tunes.”

Digital photos of hundreds of pages of sheet music arrived on a memory stick at the Yiddish New York gathering in 2017, but the crowd-sourced effort to turn them into PDF files and share them on the web didn’t get going in earnest until late 2020. In the last couple of years, several albums featuring the resurrected klezmer tunes have been recorded. Crowder estimates that at least 72 musicians have digitized at least one tune for what has been dubbed the Kiselgof-Makonovetsky Digital Manuscript Project (KMDMP).
The project is working with a total of close to 1,400 tunes from two different sources: 26 notebooks of melodies collected by Zusman Kiselgof, a Russian folklorist who participated in the seminal An-ski ethnographic expeditions, and a 236-page manuscript by Avraham Yehoshua Makonovetsky, a Russian klezmer violinist who played at Jewish weddings. Both Kiselgof and Makonovetsky were Jews. The notebooks and the manuscript had been sitting in the Vernadsky National Library of Ukraine.
“This is of incredible value,” Lyudmila Sholokhova, curator of the Dorot Jewish Collection at the New York Public Library, told me. She inventoried the Edison wax cylinder recordings of the Kiselgof collection when she worked at the Vernadsky and wrote her doctoral dissertation on early efforts to collect Jewish music in the Russian Pale of Settlement.
“This is a lot of unknown music and it also gives you a good idea how this music was actually played,” she said of the Kiselgof-Makonovetsky collection. A small number of the tunes has been circulating in recent years before the KMDMP began.
The mixed blessing of COVID-19
The COVID-19 lockdown turned out to be a blessing for the KMDMP because klezmer musicians were unable to play gigs or rehearse with their bandmates. So, they went to work digitizing the klezmer treasure trove.
“In the beginning during lockdown, you couldn’t go out to a gym, you couldn’t go play music with people. In the evening you can’t practice at home because there are neighbors. So, you digitize tunes,” Hannah Ochner told me.
The German klezmer clarinetist now lives in England and fronts a klezmer ensemble called Hop Skotshne. Ochner, 33, has a doctoral degree in physics and her main gig is researching electron microscopy in Cambridge. But she still found time to digitize an estimated 600 tunes over the course of a year and a half.
“It became addictive,” she said.

One of the untitled tunes Ochner worked on was a skotshne, a lively klezmer dance melody. The digital photo she worked from depicted a crumpled page, necessitating quite a bit of reconstruction.
“The length of the notes I left was longer than the music score,” she said.
The tune, Hannah’s Skotshne, was named in her honor.
Crowder said some of the hand-written scores were “a real mess.”
“You have to be a special kind of nerd to want to dive into this stuff,” she told me. “You’ve got four tunes crammed on the page and there’s mistakes and there’s all kinds of random old school notation.”
Crowder estimates that in addition to klezmer nerds like Ochner, a pool of more than 200 volunteers has helped by translating Russian or Yiddish text on sheet music or joined bi-weekly Zoom sessions where musicians play along with Crowder as she goes through tunes on her accordion.
The KMDMP now has at least a thousand klezmer melodies available for download as PDF’s, and Crowder said there are plans to publish a scholarly edition of some Kiselgof-Makonovetsky tunes as bound volumes. The Klezmer Institute is also planning to commission piano accompaniments for the many virtuosic solo violin pieces in the collection.
“They would be a lot of fun for a classically trained violinist to approach and to put into their own repertoire,” said Crowder. “Violin players don’t want to play clarinet pieces because they’re clarinet pieces.”
Music with global appeal
The KMDMP repertoire has been spreading at klezmer festivals in Europe and North America. The New York-based trumpeter Jordan Hirsch has passed them on to students at KlezKanada and Yiddish New York. Susi Evans and Szilvia Csaranko, a klezmer duo based in the UK and Germany, have taught the tunes at Shtetl Berlin jam sessions and Yiddish Summer Weimar, Europe’s major klezmer and Yiddish culture gathering.

Csaranko, an accordion player, is the musical director of Klezmerorchester Erfurt, an 80-piece amateur ensemble in Germany that performed a concert of the Kiselgof-Makonovetsky repertoire in 2022 before an outdoor audience of 3,000.
Evans, a clarinetist who has performed as a soloist with the BBC Scottish Symphony Orchestra, told me: “If you’re teaching klezmer music regularly, you’re always looking for tunes that someone who’s come into the workshop and knows a lot of tunes, won’t know.”
Their double CD, Fun an Altn Klezmer Heft, features 44 Kiselgof-Makonovetsky tunes, including “Hannah’s Skotshne.”
“Wherever we go, we like to spread these melodies,” Csaranko told me. “People do play these melodies they heard from us in jam sessions, in different countries. People in Australia are playing them now because they were in our workshop.”
The classically-trained clarinetist Angelo Baselli in Bologna, Italy teamed up with the accordionist Gianluca Casadei to record Fun a Velt Vos iz Nishto Mer, Of a World That Is No More. The album features Kiselgof-Makonovetsky tunes.
In a telephone interview Baselli, 47, said he caught the klezmer bug nearly 30 years ago after listening to Don Byron Plays the Music of Mickey Katz.
“I don’t have a Jewish family but instantly I fall in love with that music,” Baselli told me. “I started to search for recordings but at that time it was a little bit hard because there wasn’t a klezmer movement in Italy.”
A musical heirloom
Two klezmer trios in the Bay Area of Northern California have Kiselgof-Makonovetsky tracks on their most recent albums, both on the Borscht Beat label. Baymele’s album is Sapling. The new Veretski Pass album, The Peacock and the Sunflower, has eight Kiselgof-Makonovetsky numbers.

The Veretski Pass accordion player, Josh Horowitz, actually went to Ukraine before the KMDMP began and brought back some of the klezmer tunes from the collection.
“They were passed around like contraband at festivals,” the band’s violinist, Cookie Segelstein, said.
Their trio is named for a mountain pass in Ukraine where Segelstein’s father was born. Her mother grew up 45 miles away in the town Munkacs, where the Munkacher Hasidic sect began. So, for Segelstein, the archive of Kiselgof-Makonovetsky tunes is like a family heirloom.
“I have no way of going back to Veretski or where my mom is from and seeing her home because it was either destroyed or other people lived there,” she told me.
Describing the process of going through the unearthed klezmer tunes, Segelstein said: “We were digging through ashes. We would never have had this kind of access to this many historical tunes. To have this trove in one place has been like winning the lottery.”