Medieval German synagogue added to UNESCO World Heritage list
The U.N. body also honored a ruins site near the West Bank city of Jericho, angering Israeli officials by describing its location as in the ‘State of Palestine.’
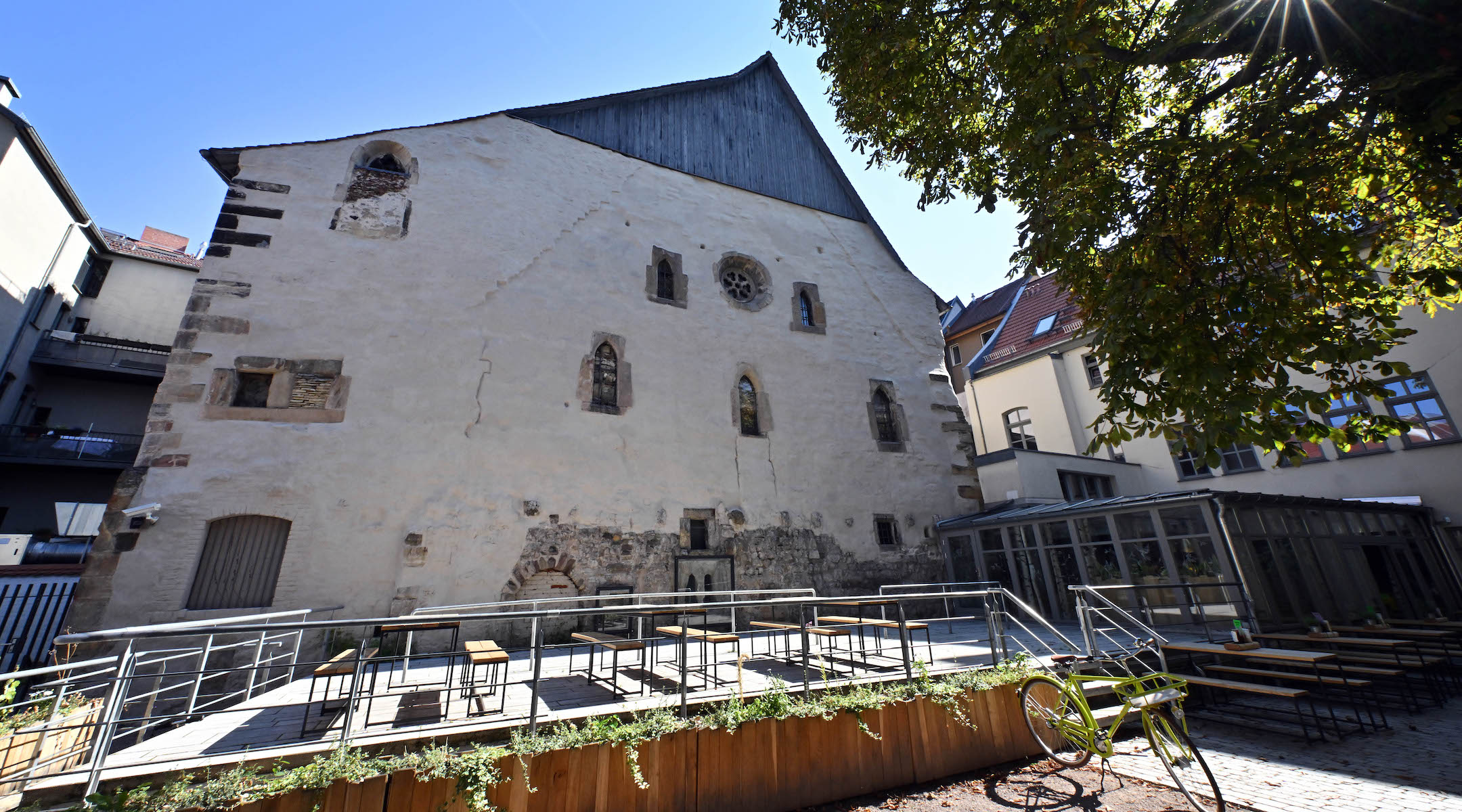

The Old Synagogue in Erfurt, Germany, seen Sept. 11, 2023, is considered one of the oldest synagogues in Central Europe. (Martin Schutt/picture alliance via Getty Images)
(JTA) — A United Nations committee designated a group of medieval Jewish buildings in Erfurt, Germany, as a World Heritage Site on Sunday.
UNESCO, the U.N. Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, also gave the World Heritage designation to a ruins site near the West Bank city of Jericho, angering Israeli officials by describing its location as in the “State of Palestine.”
The designation in Erfurt, a former East German city, was cause for celebration — the announcement, which came at the close of Rosh Hashanah, was broadcast live at the local city hall, where applause broke out. Three buildings were honored by the Paris-based U.N. agency: Erfurt’s Old Synagogue, which dates back to the late 11th century; a mikveh, or ritual bath, which is now situated under a newer building; and a 13th-century stone building that captures what Jewish life was like there in medieval times.
The announcement was good news for the new year, according to Reinhard Schramm, chairman of the Jewish regional organization for the state of Thuringia. Speaking to local media, he expressed thanks to all those who had worked on the application and said his delight at the news was tempered by worries about growing nationalism and antisemitism.
“It is important for Jews to feel that they are welcome in Erfurt,” he said. There are about 650 Jews living in the entire state of Thuringia today.
The Old Synagogue dates back to the 1090s, when its first stones were laid. A pogrom in 1349, triggered by antisemitic canards blaming Jews for the Black Plague, wiped out the entire local Jewish community. Exact numbers are unavailable, but historians say those who were not killed were either driven out or took their own lives. Researchers also suggest that the synagogue’s use as a warehouse, restaurant and dancehall over the centuries may have been what kept the Nazis from destroying it.
There were 831 Jews in Erfurt before Hitler seized power; after the war, under East German control, the city counted some 120 Jews. A new synagogue was opened in 1952.
In 1988, the forgotten synagogue was rediscovered by the Independent Institute for Building Research and Documentation. Ten year later, the city bought it from its then-owner, who had wanted to establish a beer hall and brewery there but never undertook renovations. In 2007, the community’s ritual bath — used as a cellar for centuries — was finally recognized and preserved.
Today, the synagogue houses a museum that contains, among other items, the so-called Erfurt treasure: a collection of jewelry, coins and other precious items that once belonged to a Jewish merchant or moneylender.
Now, Erfurt reportedly plans to construct a World Heritage Center near its city hall. There also is a proposal to move the Jewish community’s center to the new site, and to open a kosher restaurant.
Kerstin Pürschel, German’s ambassador to UNESCO, called the body’s decision an important step toward honoring the common roots of Judaism and Christianity in Germany. It is the second Jewish site in Germany to be protected by UNESCO: Two years ago, they added locations in the Rhine River cities of Mainz, Worms and Speyer — seen as a region where Yiddish first developed — to the list.
The West Bank city of Jericho, controlled by the Palestinian Authority, is seen as one of the world’s oldest continually lived in places. A spring still in use near the prehistoric ruins site was included in the UNESCO recognition.
“The natural resources and strategic location of Ancient Jericho/Tell es-Sultan made it … a major node of human development for millennia,” the Palestinian Tourism and Antiquities Ministry wrote to UNESCO, according to The Washington Post. “Today’s residents drink water from the same springs and irrigate the same fields” as ancient Jericho residents.
Israel’s foreign ministry blasted UNESCO’s decision in a statement, calling it “another sign of the Palestinians’ cynical use of UNESCO” and the “politicization of the organization.” Israel, which has nine World Heritage sites, left UNESCO in 2019, citing what it calls the U.N. body’s bias in its description of Palestinian and Israeli sites.
This article originally appeared on JTA.org.