I’m a neuroscientist. Here’s why Ahmed al Ahmed’s bravery at Bondi Beach strains our narratives.
In a world seemingly defined by group loyalty, al Ahmed stands out, writes a neuroscientist
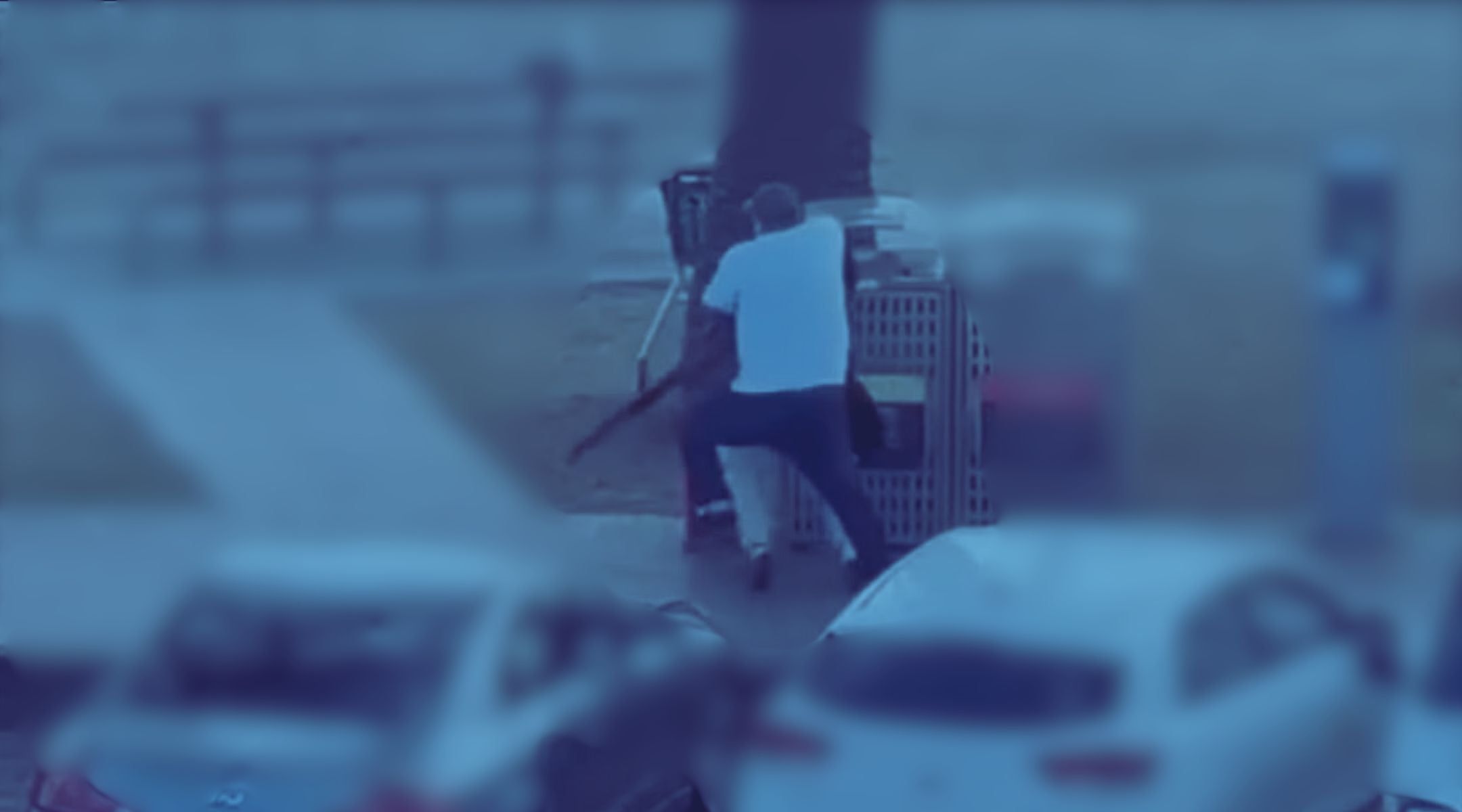

Ahmed al Ahmed’s effort to halt a terrorist attack on a Hanukkah celebration in Sydney, Australia, has made him a hero. Graphic by JTA
(JTA) — We tend to think of human behavior as deeply shaped by group lines. Again and again, research in social psychology and social neuroscience, along with everyday experience, shows how easily people come to see themselves as members of distinct groups, how quickly an “us” and a “them” emerge, and how rapidly loyalty on one side gives way to suspicion on the other, sometimes even when those divisions are thin or arbitrary.
As a fiction writer and a doctoral student in cognitive neuroscience who studies how narratives shape our perception of the world, I think often about how events like this strain the explanatory stories we rely on to make sense of why people act as they do. These patterns of group loyalty are familiar and empirically robust. People genuinely experience themselves through group identities.
And yet sometimes a single human action cuts across these categories, exposing the limits of the narratives we use to understand how people act in the world.
That is what we have experienced this week in the story of Ahmed al Ahmed, the Muslim fruit-seller who intervened, at great personal risk, to try to stop a deadly attack on Jews celebrating Hanukkah in Sydney.
Al Ahmed’s action was not only an act of exceptional bravery, but a direct challenge to the worldview advanced by so many figures today. By knowingly risking his life to protect Jews outside his own group and identity, he crossed the very boundary that many insist cannot be crossed, revealing a simple truth: that human moral action cannot be reduced to rigid theories of group loyalty alone.
Perhaps one of the most prominent proponents of a growing online current that frames human life as fundamentally governed by group identity is the white supremacist livestreamer Nick Fuentes. He has repeatedly advanced antisemitic claims, arguing that Jews are incapable of full civic loyalty, that they put their own group first, and that Jewish Americans are ultimately more loyal to Jews as a group or to Israel than to the United States itself. He has said about Jews, “They have this international community across borders, extremely organized, that is putting the interests of themselves before the interests of their home country.” In Fuentes’ framing, human existence is a competition between groups, and moral loyalty is by definition exclusive. He is careful to insist that these claims are not antisemitic, presenting them instead as a hard-headed and honest description of human nature.
A similar logic appears in the rhetoric of Thomas Rousseau, the leader of the extremist group Patriot Front, who describes the United States as being locked in an inevitable racial struggle. Rousseau has framed this worldview in stark terms, declaring that white people are “being relentlessly erased on all sides, by the Jew, by non-whites who hate us,” a statement that casts social and political life as an existential battle between fixed identities.
But the worldview advanced by figures like Fuentes and Rousseau collapses when confronted with a single human act such as that of Ahmed Al Ahmed. If human life were truly governed only by intergroup competition and instinct, there would be no room for a person to knowingly risk his life for strangers from another group, let alone in the midst of mortal danger. Yet this is precisely what happened. Al Ahmed risked his life to protect members of a group to which he did not belong. This altruistic act directly contradicts the theories advanced by Fuentes and Rousseau and exposes them for what they truly are, not neutral descriptions of reality but ideological narratives imposed upon it. Beneath the edgy aesthetics, viral memes, and provocative social media packaging, these claims amount to recycled pseudo-intellectual arguments, longstanding tropes of racism and antisemitism that have circulated throughout history under different guises.
Understanding Al Ahmed’s act, however, requires moving beyond abstract theory to the explanations offered by those closest to the event. Two interpretations have emerged in media accounts of why he risked his life. One, expressed by his father, presents the act in simple and universal terms. His father said that “Ahmed was driven by his sentiment, conscience and humanity.” The other explanation, voiced by Lubaba Alhmidi AlKahil from within the Muslim and Syrian community after visiting Al Ahmed in the hospital, situates the act within a specific moral culture and identity. As she put it, this kind of response is “not strange for a Syrian individual,” coming from a community with strong bonds that has learned to refuse injustice. What is striking is that these two explanations can exist side by side without canceling one another, a possibility that figures like Nick Fuentes and those who share his worldview struggle to grasp because they are locked into a rigid, binary understanding of human motivation.
One might argue that Al Ahmed’s act was a rare exception in a world otherwise governed by group conflict and self-interest. But the reality is that every day, people risk their lives to protect others across lines of identity. Adam Cramer dove into the water to save a drowning girl. Lassana Bathily hid Jewish shoppers during the Hyper Cacher attack in Paris. Mamoudou Gassama saved a child he did not know. Wesley Autrey jumped onto subway tracks to rescue a stranger, and Henri d’Anselme confronted a knife attacker to protect children. Seen in this light, Ahmed Al Ahmed stands within a long human tradition that includes, even in more distant history, figures such as Raoul Wallenberg and Chiune Sugihara, who risked their lives to save others during the Holocaust.
Evolutionary research itself points in the same direction. Across species, altruistic behavior appears again and again, from dolphins that keep injured companions afloat so they can breathe, to rats that will free trapped cage mates. Far from an anomaly, altruism is a recurrent feature of social life, and our brains have a remarkable capacity for empathy and for understanding the experiences of others, far beyond the lines of group identity and social belonging. Fuentes and those like him may insist that people are loyal only to their own group, but reality erodes this impoverished and intellectually lazy theory on a daily basis.
Crucially, these acts do not testify only to universal altruism abstracted from identity. In many cases, they emerged from deeply held group identities and moral traditions. Cultural, religious, and national affiliations did not prevent these individuals from acting on behalf of others. They often supplied the very moral language and sense of responsibility that made such action possible. Universal concern and particular identity therefore do not stand in opposition. They coexist, with specific histories serving not as barriers to moral action but as sources from which it can arise.
That is precisely what figures like Nick Fuentes and those who share his worldview fail to account for. Their politics rests on a rigid vision of identity as a closed framework, one that leaves no room for moral action that crosses its prescribed boundaries. The horrific attack at Bondi Beach, and the courage of Ahmed Al Ahmed within it, remind us that moral action often arises neither from abandoning identity nor from clinging to it defensively, but from inhabiting it fully while remaining open to others.
In an age shaped by clickbait, algorithms and relentless simplification, such moral complexity is difficult to sustain. Political arguments reward camps and slogans. But the actual behavior of people like Ahmed Al Ahmed escapes the internet’s simplified categories and points instead toward a richer form of conduct, one that can be called, quite simply, humanity.
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of JTA or its parent company, 70 Faces Media.