In Brigitte Bardot, a complicated legacy of movie stardom, activism, xenophobia and antisemitism
Bardot, who has died at 91, lurched to the right after she retired from motion pictures in 1973
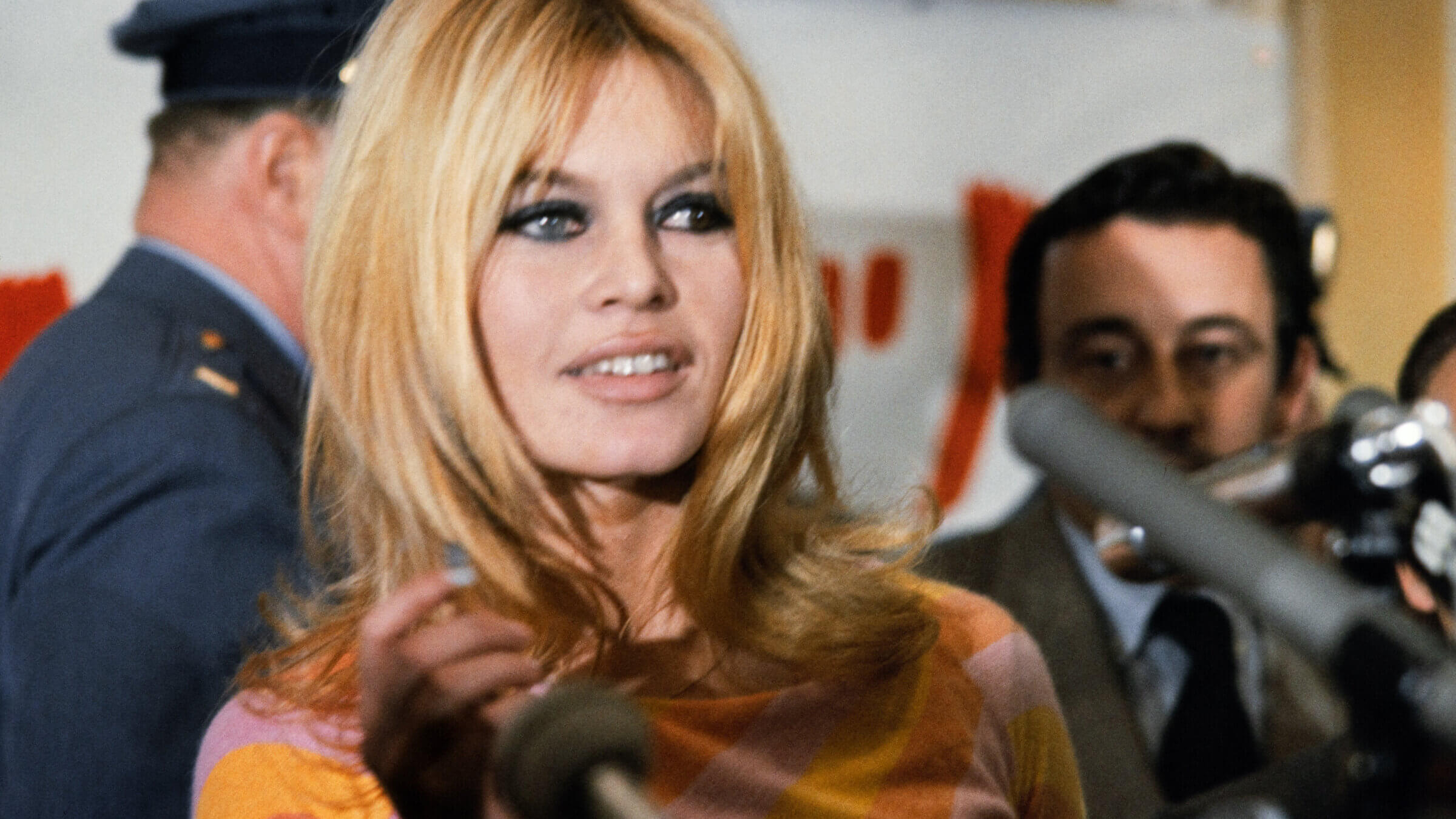

Brigitte Bardot gives a press conference on December 1965. Photo by AFP via Getty Images
The French actress Brigitte Bardot, who died Sunday at the age of 91, leaves behind a legacy as an actress who starred in a few notable and many less than notable films. Perhaps more importantly, Bardot also starred as BB (pronounced, bien sûr, as “baby”), a cultural icon who embodied the glories and miseries of a rapidly modernizing postwar France.
Life is short, art is long, and politics is, at times, even longer. At least, this is true for the life of Bardot. Bardot burst upon the world stage in 1956 with élan (and an ellipsis) upon the release of “Et Dieu…créa la femme” and made her last film “L’Histoire très bonne et très joyeuses de Colinot” in 1973. This makes for a movie career that spanned 17 years. If we were than to subtract 1973 from 2025, we get 52 years.
But during the 52 years Bardot lived following her retirement from cinema, the world witnessed a different kind of spectacle, one which shifted from the aesthetics of Bardot as a pop phenomenon during the 1950s — she was described by Simone de Beauvoir, in an Esquire essay, as “the most perfect specimen of the ambiguous nymph” — to Bardot’s downwardly spiraling politics in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
A starting point to think about Bardot and politics — or, better yet, ideology — is 1969. While France was still reeling from the student rebellion of 1968, an event that nearly brought down the government of Charles de Gaulle, Bardot was named as the model for “Marianne,” a mythic figure who was, and remains, the personification of the French republic built on the revolutionary values of 1789.
Bardot remained the model for several years, with postage stamps of her likeness on countless envelopes and busts in city halls across the country. In 1985, however, Catherine Deneuve became the face of Marianne. The two stars tended to play very different kinds of roles in their films: Bardot’s barely tamed sexuality contrasted sharply with the mesmerizing iciness of many of Deneuve’s characters.
As time passed, the two Mariannes revealed very different political values. In 1971, Deneuve signed the history-changing “Manifesto of 343 Women,” which supported the legalization of abortion, and has spent her life in the republican camp — an opponent of the death penalty and a part of the “republican wall” formed against Jean-Marie Le Pen during the 2002 presidential elections.

Meanwhile, Bardot’s politics veered ever more rightward until they could veer no further. In 1992, Bardot attended a dinner in Saint-Tropez — the sleepy Provençal port she turned into, well, Saint-Tropez — hosted by Jean-Marie Le Pen’s second wife, Jany Le Pen. Another guest was Jean d’Ormale, a shadowy businessman and a close advisor of Le Pen, who soon became Bardot’s fourth and final husband. Bowled over by Bardot, Le Pen recalled, “Compared to Bardot, Marilyn Monroe looked like a bar waitress.” He added that he and Bardot had much in common: “She loves animals and misses the France that was clean and proper.”
In her own memoir B.B., Bardot returned Le Pen’s compliment. He was, she wrote, “a charming and intelligent man who was revolted by many of the same things I was.” For the next two decades, Bardot’s righteous campaign against animal cruelty was entwined with her noxious campaign against Muslim immigrants. Her hatred of the Muslim preparation of halal meat transmogrified into a hatred of Muslims, period. From the late 1990s and late 2000s, Bardot, who persistently railed against the Muslim “invasion” of France, was convicted several times by French courts of inciting racial hatred.
Inevitably, her visceral loathing of ritual slaughter bled into antisemitism. In 2014, Bardot was widely criticized for her description of kosher and halal traditions as “ritual sacrifice.” Moshe Kantor, the president of the European Jewish Congress, ripped into this phrase, declaring it was “deeply offensive and a slur against the Jewish people.” Kantor noted that while Bardot “may well be concerned for the welfare of animals, her long-standing support for the far right and for discrimination against minorities in France shows a constant disdain for human rights instead.”
In a eulogy posted on X, President Emmanuel Macron observed that “with her films, her voice, her dazzling glory, her initials (BB), her sorrows, her generous passion for animals, and her face that became Marianne, Brigitte Bardot embodied a life of freedom…We mourn a legend of the century.” All of this is true, but it is equally true that BB embodied yet other sorrows and passions that cast a lengthening and darkening shadow over this century.