Israeli immigration records now searchable in English online
Do you have a family member who made aliyah? You may be able to find their documents
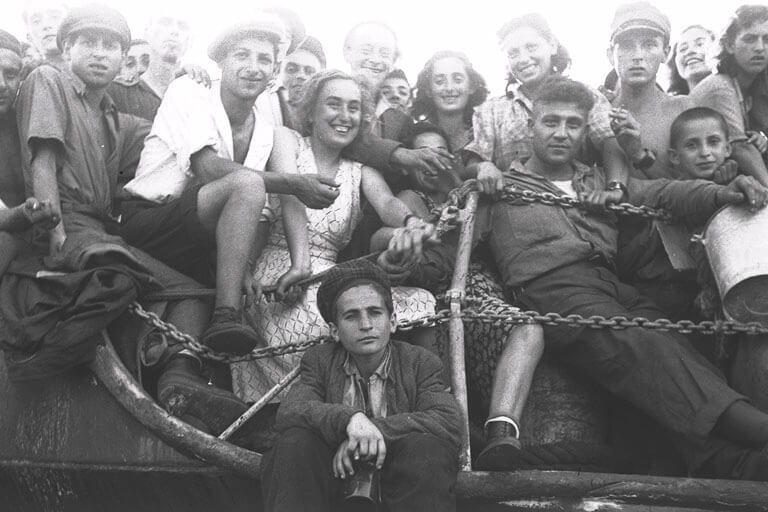

A crowd of Jewish immigrants smile as they arrive at Haifa harbor in 1947. Photo by AFP via Getty Images
A vast database of Israeli immigration records is now online with a searchable index in English.
The collection of 1.7 million records, published by MyHeritage.com, is free for anyone to search. The database includes scanned images of documents for immigrants who arrived in Israel from 1919 on, from anywhere in the world, by ship, plane or land. The records include the immigrants’ names; names of those who traveled with them and those who were expecting them in Israel; country of origin; date of arrival and their destination city.
The collection will be a boon not just for genealogists but for anyone looking to fill in gaps in their family history for a relative who made aliyah.
Jennifer Mendelsohn was able to find her grandfather’s brother, Itzhak Jäger, arriving with his family in 1933, “which was poignant,” she said. He emigrated from what was then Poland and is now Ukraine, and lived out his life in Israel.
Four distinct waves
The collection includes immigration records for four distinct waves, starting with the British occupation of Palestine in the aftermath of World War I, through Israeli statehood and beyond.
The earliest wave consisted of Jewish immigrants, called halutzim, or pioneers, who started new lives in Israel between 1919 and 1923. They were motivated by antisemitism and lack of opportunity at home following World War I, along with support for the Zionist cause.
The next wave, from 1924 to 1929, mostly moved to Israel to escape rising antisemitism in countries like Poland, the Soviet Union, Romania and Lithuania, but also included Jews from Yemen and Iraq.
Those who arrived between 1929 and 1939 emigrated from Poland, Germany, Austria, Czechoslovakia and Greece — many of them fleeing the Nazis’ rise to power — along with immigrants from Turkey, Iran and Yemen.
A fourth wave consisted of Jews who moved to Palestine under Britain’s strictly enforced quotas between 1933 and 1948, including those who managed to survive the war. Jews who entered the country without legal documentation are not included in the records.
The records consist of scanned images from books in the Israel State Archives listing immigrants in chronological order by arrival. You can search for names in English and other languages and read some key details without knowing Hebrew, but the complete scanned documents are in Hebrew.
Examples of individuals whose records have been unearthed provided by MyHeritage include Bracha Fuld, one of the first female Jewish soldiers killed during the British conflict before statehood. A street is named after her in Tel Aviv. She arrived in Haifa in 1939 from Germany at age 13. Another example is Austrian swimmer Judith Deutsch-Haspel, who set records in her sport but refused to represent Germany in the 1936 Olympics. She emigrated in 1938 with her parents and sister and eventually became a swimming champion in Israel.
CORRECTION: This story has been corrected to show that the records do not end in 1949. The story has also been updated to clarify that Itzhak Jäger emigrated from what was then Poland and is now Ukraine.

















