What happened in Israel? The Hamas attack, its grim toll and what’s next, explained
Nothing like this has ever happened in Israel, and Israelis are comparing the day to 9/11 — and asking how their vaunted military could have been so unprepared for such a major assault.
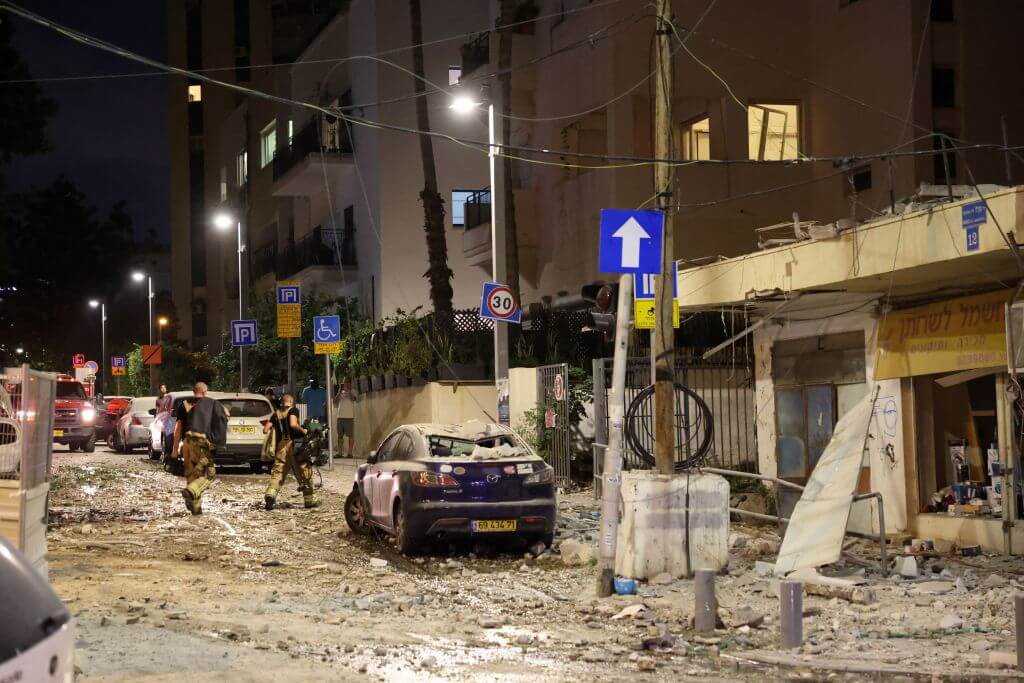

Members of the Israeli security forces walk along a debris-strewn street in Tel Aviv, after it was hit by a rocket fired by Palestinian militants from the Gaza Strip on October 7, 2023. Photo by Getty Images
(JTA) — Saturday was a day of bloodshed unprecedented in Israel’s history.
Beginning in the morning of a Jewish holiday, hundreds of militants broke through the barrier between Israel and Gaza and spread into more than 20 locations, killing 300 Israelis on the streets, in their homes and at an outdoor festival, taking some 100 hostage and injuring more than 1,800.
In a country whose chronology is punctuated with wars, terror attacks and military offensives, Saturday stood out in its horror. Nothing like this has ever happened in Israel, and Israelis are comparing the day to 9/11 — and asking how their vaunted military could have been so unprepared for such a major assault.
Nearly a day after they invaded, the militants — sent by the terror group Hamas — appear to have been mostly but not entirely cleared out of Israeli territory. But the fighting is just beginning. While the day’s grim tally is not yet clear, a huge number of Israelis have been taken hostage in Gaza, and Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu is promising an unmitigated war on Gaza, which has seen repeated rounds of conflict with Israel over the past 15 years.
“Hamas has launched a cruel and evil war,” Netanyahu said in a televised address. “We will win this war, but it will carry a very heavy price. This is a difficult day for all of us.”
Is this the worst Israel-Hamas fighting?
Hamas, a Palestinian terror group, has launched attacks on Israeli civilians for decades and has governed the Gaza Strip for more than 15 years. During that time, it has launched barrages of missiles at Israeli cities on the Gaza border and beyond, sending residents fleeing for shelter, and Israel has responded with airstrikes and offensives that have killed thousands of Palestinians in the coastal strip.
Israel launched ground invasions of Gaza in 2008 and 2014. The most recent major round of conflict between the two sides took place in 2021.
But Hamas has never attacked Israel as it did on Saturday. While it has previously built a network of tunnels to infiltrate Israel, Saturday’s invasion was on a much larger scale. Militants broke through a barrier built by Israel, attacked by sea and began killing people in 20 different cities and towns. Makeshift bands of Israeli civilians battled the Hamas operatives while the Israeli military belatedly mobilized.
The militants also took a large number of hostages back to Gaza, in addition to holding hostages in a kibbutz cafeteria and a private home in Israel.
They captured two ambulances and an Israeli tank. They took control of the police station in the border city of Sderot for some 20 hours. They overran an Israeli military base.
A portion of the violence, and many of the graphic videos circulating on social media, came from an all-night party near the border, where revelers fled Hamas, but where some were taken captive into Gaza.
Along with the ground invasion, Hamas sent volleys of missiles at targets across the country.
By the end of the day, the official death toll had reached 300 — including many civilians and the commander of the Israel Defense Forces’ Nahal Brigade, one of the most senior Israeli military officials to be killed in recent years.
That is a stark contrast with the rocket fire which — due in part to Israeli warning and missile defense systems — has historically had a low civilian death toll. Saturday was one of the bloodiest days in the history of israel.
How has the IDF responded?
Israeli-Palestinian violence has escalated all year, but the epicenter of that fighting has been in Jerusalem and the West Bank, not Gaza. A flareup of fighting between Hamas and Israel earlier this year ended after five days.
But as the day progressed, it became clear that Hamas’ attack took Israel by surprise. Residents of the small cities and kibbutzim on the border, absent any help by the IDF, resorted to forming armed bands and attempting to clear out the Hamas fighters themselves. A senior local official was killed while trying to defend his town.
A day after the attack started, it appeared the IDF had regained control over the area. But that was after 24 hours that included news no Israeli expected to hear: that Hamas had taken control of an army base and police station; that it had captured military and medical vehicles; and that it had taken hostages to Gaza.
The invasion came as Israel’s government has been occupied with other matters, including a contentious effort to weaken Israel’s court system and a possible diplomatic accord with Saudi Arabia. The future of those initiatives is unclear. Instead, exactly 50 years after Israel was caught by surprise by the invasions that began the Yom Kippur War, the country was once again asking how this could have happened.
“These days there’s no king in Israel,” Haaretz reporter Amir Tibon posted online, quoting a Bible verse meant to evoke a sense of disorder. “Take care of yourselves.”
What will happen to the hostages? Does Israel negotiate for hostages?
According to Israel’s Foreign Ministry, 100 Israelis have been taken by Hamas and brought into Gaza. If that number, or anything of its magnitude, is accurate, it would be many more than the group has ever captured.
Hamas kidnappings have, in the past, led to Israeli military operations and to at least one prisoner exchange.
In 2006, Hamas took one soldier, Gilad Shalit, hostage. Israel sent troops into Gaza following his capture but was unable to recover him. Soon afterward, the Lebanese terror group Hezbollah took two other Israeli soldiers captive in an incident that launched the 2006 Lebanon War.
Five years later, in 2011, Shalit was freed in an exchange with a controversial legacy: Nearly 1,000 Palestinian prisoners were released in return for the soldier. Indirect negotiations between Israel and Hamas led to the deal.
Three years after that, in 2014, some of the Palestinian prisoners released in the Shalit deal were involved in another kidnapping of Israelis — the abduction and subsequent murder of three Israeli teens in the West Bank. That incident led to the 2014 Gaza War, which saw Israel invade the territory and lasted 50 days.
If Hamas has abducted 100 Israeli civilians and soldiers, it will be another element of Saturday’s violence with no precedent in history, though in 1976, Palestinian hijackers took more than 100 hostages at Entebbe Airport in Uganda. Nearly all of those hostages were freed in a famous operation in which the only Israeli soldier to die was Yoni Netanyahu, the current prime minister’s brother.
What will happen next?
Little is clear except that Israel’s leaders have promised a large-scale war in Gaza.
“The IDF will immediately activate all of its capabilities to destroy Hamas’ abilities,” Netanyahu said Saturday. “We will forcefully avenge this black day they have forced upon Israel and its citizens.”
That almost certainly means a ground invasion of Gaza, which promises to bring more death and destruction. Israeli airstrikes on Gaza have already reportedly killed more than 200 people, and masses of reservists have been called up.
It is too soon to tell how long the coming war will last or how wide-ranging it will be. The last ground invasion of Gaza, in 2014, lasted 50 days and ended with more than 70 Israelis and more than 2,100 Palestinians dead.
To conduct the new campaign, centrist Yair Lapid, the leader of Israel’s parliamentary opposition, has called for Netanyahu to form an emergency government that would include centrist parties as well as his current religious and far-right partners. Such an emergency government was also formed during the Six Day War in 1967.
An emergency government including opposition parties would likely spell an end — or at least a significant pause — for the issue that until Saturday was causing widespread strife in Israel: the government’s judicial overhaul. A government with centrists would not approve such an overhaul, and it is less likely to move forward in the middle of a war. Protests against the overhaul have likewise been put on pause.
What this means for Israel’s talks with Saudi Arabia is also unclear, but any deal between the two countries was meant to include Israeli concessions to the Palestinian Authority — something Israel would likely be less inclined to agree to while fighting in Gaza.
“At this moment, I won’t address who is to blame or why we were surprised,” Lapid said in a video message. “This is not the time or the place. We will stand united against our enemies. Israel is at war.”
This article originally appeared on JTA.org.