After 2-year delay, Philip Guston art exhibit explores his Jewish identity — under cloud of controversy

Paintings such as “The Studio” (Oil on canvas, 1969) had museum curators rethink how to present Guston’s work. (Private Collection/© The Estate of Philip Guston, courtesy Hauser & Wirth/Courtesy Museum of Fine Arts, Boston)
BOSTON (JTA) — Many visitors to the newly-opened Philip Guston (born Goldstein) exhibit at the Museum of Fine Arts Boston will not go in knowing how his Jewish experience influenced his work: from his roots as the son of Jewish immigrants to his youthful encounters with antisemitism, to the ways in which the Holocaust emerged as a theme in his art making.
Instead, many will undoubtedly have some knowledge of the controversy that has swirled around it for nearly two years — which is hinted at in the exhibit itself.
One of the most influential artists of the last century, Guston’s style over 50 years swung from figurative to abstract expressionism and back to figurative in a prolific body of work that confronted the evils of society, often drawing on irony and humor. “Philip Guston Now,” which in its Boston iteration consists of 73 paintings and 27 drawings, was first slated to open in the summer of 2020. After a COVID delay, it was held back again months later, in September, after the directors of the museums that the exhibit would travel through — the National Gallery of Art in Washington, the Tate Modern in London, the MFA Boston and the Museum of Fine Arts Houston — expressed concern about how Guston’s work, notably his striking cartoon-like images of hooded Ku Klux Klan figures, would be received amid the nationwide reckoning with racial injustice.
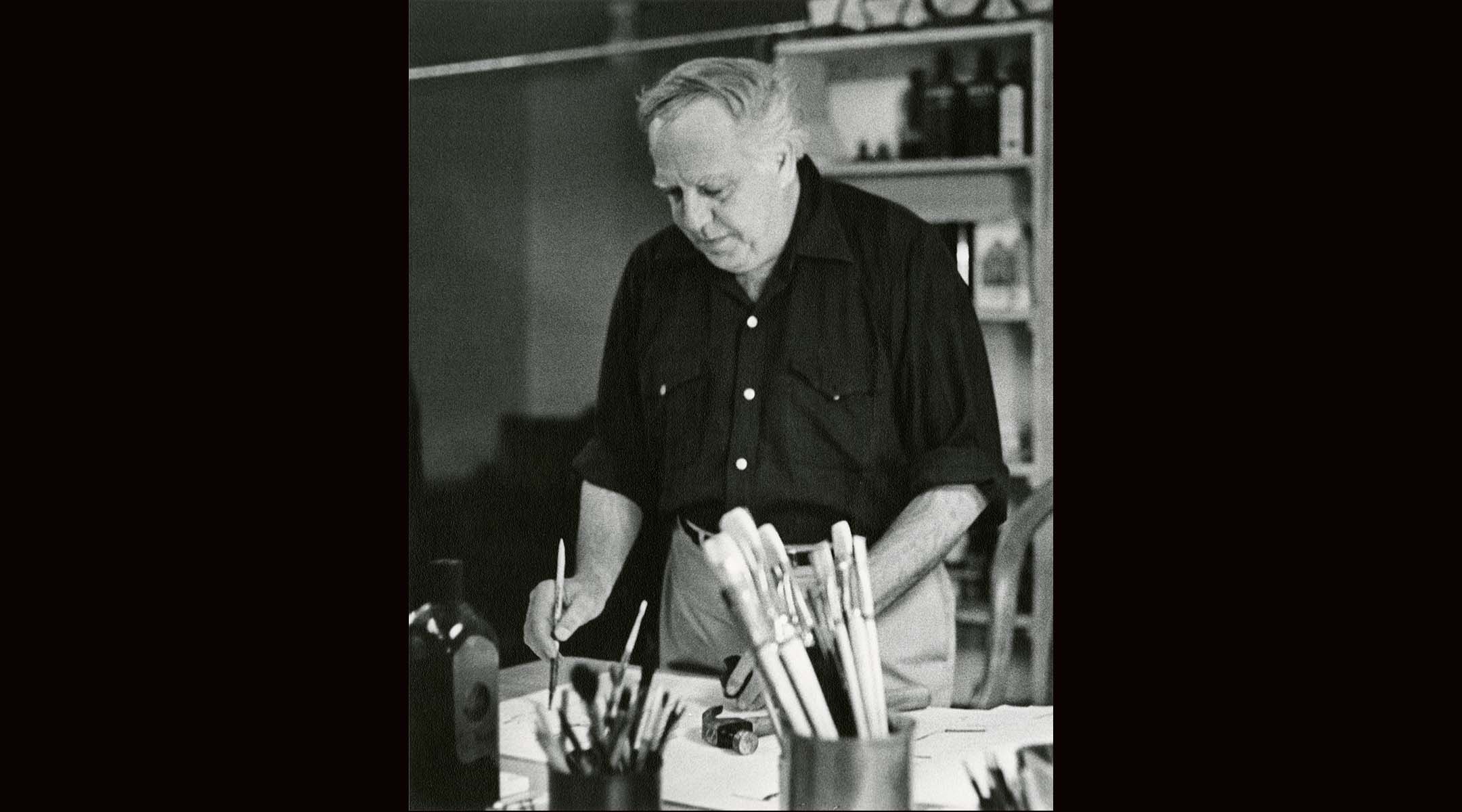

Philip Guston in his studio in 1970. (Photo: Frank K. Lloyd, Courtesy of The Guston Foundation/Courtesy Museum of Fine Arts, Boston)
It was only a few months after the murder of George Floyd by police in Minneapolis shook the world and led to protests against pervasive racism across the country. The museums delayed the exhibit until 2024, “until a time that the powerful message of social and racial justice that is at the center of Philip Guston’s work can be more clearly interpreted,” they said in a statement at the time.
Critics accused the museums of censoring Guston’s challenging art. Defenders insisted that the changed cultural and political context required rethinking the way Guston’s art should be presented. A group of 100 artists and curators protested the move, calling on the museums to “do the necessary work to present this art in all its depth and complexity.” The list of signatories grew to more than 1,000.
The exhibit has now opened well before 2024, on May 1 in Boston, in a shuffling of the show’s touring schedule, with a heaping of historical context. Visitors are cautioned about the powerful emotions of the exhibit and are given choices at various points of what to see, as well as an exit point. Photographs and archival material of brutal violence against Blacks and others of Holocaust victims that relate to Guston’s work are in display cases beneath sliding covers, offering viewers the option of whether to see them. A pamphlet written by a trauma specialist says visitors should “identify your boundaries and take care of yourself.”
Organized thematically, curators also weave in the narrative of Guston’s biography, a key takeaway from the Boston MFA’s advisory group, according to Kate Nesin, the museum’s guest curator who has been working on the exhibit for some four years. A timeline that traverses personal and historical events hangs on the walls throughout the galleries.
“[Guston’s] biography, including his name change … is how we understand his relationship to the self reckoning we see in these paintings,” Nesin told the Jewish Telegraphic Agency at a preview.
The exhibition catalog, published in 2020, includes two essays that highlight Guston’s Jewish identity, one by Harry Cooper, head of modern and contemporary art at the National Gallery and another by Mark Godfrey, then at the Tate, who was one of the show’s four curators. Art Spiegelman, author of “Maus,” weighs in with an artist’s essay about the influence of comics on Guston’s work.
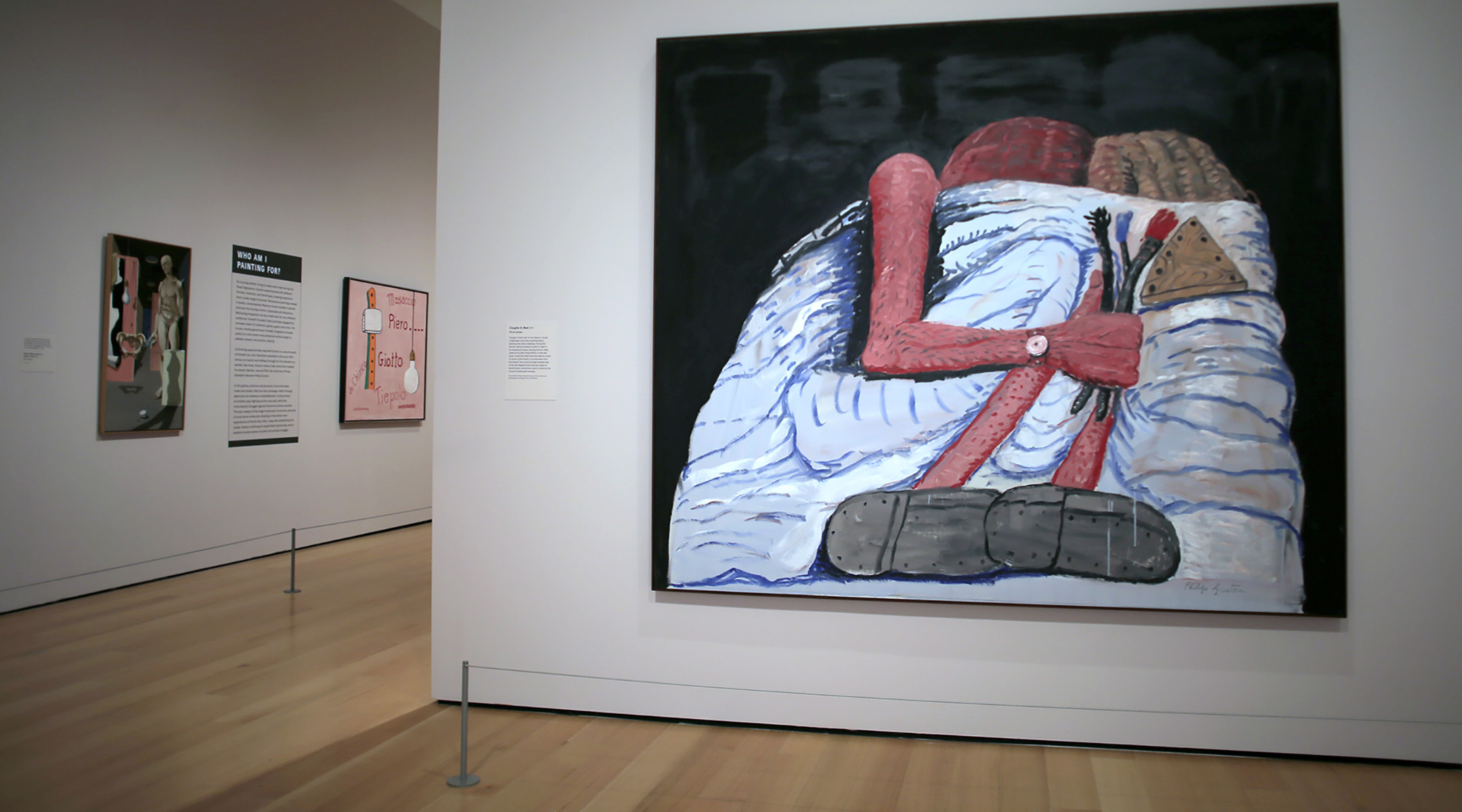

A view of the Philip Guston painting “Couple in Bed” (1977) is seen at a major show at the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, April 27, 2022. (Lane Turner/The Boston Globe via Getty Images)
Guston (1913-1980), was the youngest of seven children — three of whom, including Guston, were born in Montreal, where his parents and older siblings first settled after fleeing Ukraine. A decade later, after the family had moved to Los Angeles, his father committed suicide by hanging, a tragedy the artist confronted through images of dangling ropes.
Guston’s lived experience and the arc of his work are pivotal to understanding his challenging images, Megan Bernard, the Boston MFA’s director of membership and one of the exhibit’s curators, told JTA in a phone conversation.
“Many outside the art world arrive at Guston through the Klan imagery. That … probably colors his work in a way that is unfair to who he was. There are many points of his life that haunt him and that he relentlessly returns to throughout his career,” she said.
Guston first achieved acclaim in the 1950s for his abstract expressionist canvases, prominent among such luminaries of the movement as William de Kooning, Mark Rothko and Jackson Pollock, a friend of Guston’s since high school.
He famously abandoned the style in a 1970 show at a New York gallery, moved by the social and political unrest of the times.
“The [Vietnam] war, what was happening to America, the brutality of the world. What kind of man am I, sitting at home, reading magazines, going into frustrated fury about everything — and then going into my studio to adjust a red to a blue?” Guston said in an oft-quoted remark from 1977.
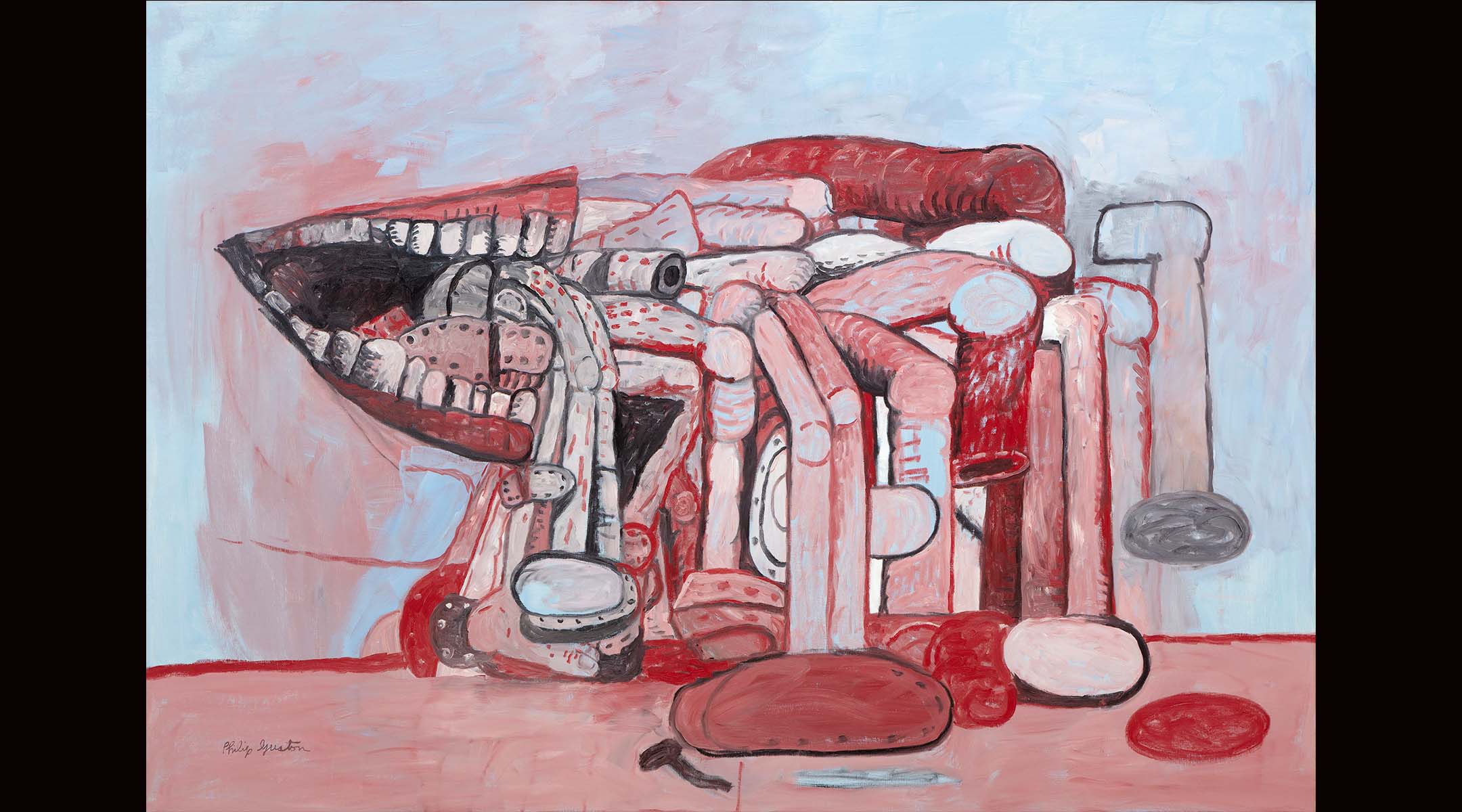

“The Black Sea” (1977), from late in Guston’s life, is part of the Odessa series, a nod to Ukraine, where his parents fled pogroms in the early 20th century. (The Estate of Philip Guston, courtesy Hauser & Wirth/Courtesy Museum of Fine Arts, Boston)
In his bold new works that featured the hooded Klan figures, Guston embraced the figurative style of his formative years; but now, years after painting the Klansmen as menacing figures in politically charged murals in the 1930s, these paintings were more ambiguous, at times comedic and deeply introspective at others.
Other works featured motifs of stick-like limbs and soles of shoes, images that evoked the Holocaust and also reflected personal tragedies that haunted Guston’s life, including the tragic accidental death of his older brother, Nat, who died from injuries after his legs were crushed by a car.
A display case with a sliding cover that can be opened by visitors reveals clippings of the larger-than-life photographs from the 1945 exhibit “Lest We Forget,” mounted by journalist Joseph Pulitzer, who visited the Nazi death camps following liberation. Viewers learn that Guston would have most likely seen the exhibit when it kicked off in St. Louis, where he was teaching at the time.
In “Porch 2,” a leg sticks up in a flattened scene with emaciated bodies, part of a series painted in 1946 that Guston said in an interview was in response to the Holocaust. The images emerged again decades later in paintings such as “Rug” (1976), where stick-like limbs and soles of shoes, in outlined reds and pinks, are piled together in form and shapes that recall the photographs of victims of the death camps.
Among the show’s other powerful later works that feature the hooded Klan figure is “The Studio,” from 1969, on display in a studio-like space within the gallery. In Guston’s palette of pinks, reds and blacks and a vibrant touch of green at the window, a hooded artist – is it Guston? – is caught red-handed, painting a canvas of the outline of another hooded figure.
The show — which will next travel to Houston, Washington, and then London, where it will close in February 2024 — ends with “Black Sea,” which is part of the artist’s Odessa series. In the contemplative painting, an arch-shaped, horseshoe-like image that resembles the shoes in Guston’s other works, floats on or emerges from a darkened sea, set against a richly layered pale blue sky. It links Guston’s past and his family’s roots to current events and the war in Ukraine.
“It embodies the idea that at the end of his life, [Guston was] looking back on a heritage he didn’t know,” Ethan Lasser, the MFA’s director of Art of the Americas and a show curator, told JTA at a preview.
It struck a strong generational chord for Lasser, who is Jewish. “It’s a nod to the Goldstein family,” he reflected.
This story originally appeared on JTA.org.

I hope you appreciated this article. Before you go, I’d like to ask you to please support the Forward’s award-winning journalism this Passover.
In this age of misinformation, our work is needed like never before. We report on the news that matters most to American Jews, driven by truth, not ideology.
At a time when newsrooms are closing or cutting back, the Forward has removed its paywall. That means for the first time in our 126-year history, Forward journalism is free to everyone, everywhere. With an ongoing war, rising antisemitism, and a flood of disinformation that may affect the upcoming election, we believe that free and open access to Jewish journalism is imperative.
Readers like you make it all possible. Right now, we’re in the middle of our Passover Pledge Drive and we need 500 people to step up and make a gift to sustain our trustworthy, independent journalism.
Make a gift of any size and become a Forward member today. You’ll support our mission to tell the American Jewish story fully and fairly.
— Rachel Fishman Feddersen, Publisher and CEO
Join our mission to tell the Jewish story fully and fairly.
Our Goal: 500 gifts during our Passover Pledge Drive!